巡风源码浅析
前言
由于一些需要,和抱着学习的目的,研读了下巡风这款相当优秀的扫描器代码。
https://github.com/ysrc/xunfeng
主要分析了下两个扫描的模块,对web端没有跟进看,当然重点也在扫描的部分。
分析的语句都以注释的形式标注在代码中了,由于能力有限,分析中的不足和错误欢迎指出。
整体架构逻辑
文件结构
│ Config.py # 配置文件
│ README.md # 说明文档
│ Run.bat # Windows启动服务
│ Run.py # webserver
│ Run.sh # Linux启动服务,重新启动前需把进程先结束掉
│
├─aider
│ Aider.py # 辅助验证脚本
│
├─db # 初始数据库结构
│
├─masscan # 内置编译好的Masscan程序(CentOS win64适用),需要chmod+x给执行权限(root),若无法使用请自行编译安装。
├─nascan
│ │ NAScan.py # 网络资产信息抓取引擎
│ │
│ ├─lib
│ │ common.py 其他方法
│ │ icmp.py # ICMP发送类
│ │ log.py # 日志输出
│ │ mongo.py # 数据库连接
│ │ scan.py # 扫描与识别
│ │ start.py # 线程控制
│ │
│ └─plugin
│ masscan.py # 调用Masscan脚本
│
├─views
│ │ View.py # web请求处理
│ │
│ ├─lib
│ │ Conn.py # 数据库公共类
│ │ CreateExcel.py # 表格处理
│ │ Login.py # 权限验证
│ │ QueryLogic.py # 查询语句解析
│ │
│ ├─static #静态资源目录
│ │
│ └─templates #模板文件目录
│
└─vulscan
│ VulScan.py # 漏洞检测引擎
│
└─vuldb # 漏洞库目录Run.sh
整个程序的开始就是从Run.sh开始的,可以先来看下起了哪些服务
#!/bin/bash
CURRENT_PATH=`dirname $0`
cd $CURRENT_PATH
XUNFENG_LOG=/var/log/xunfeng
XUNFENG_DB=/var/lib/mongodb
[ ! -d $XUNFENG_LOG ] && mkdir -p ${XUNFENG_LOG}
[ ! -d $XUNFENG_DB ] && mkdir -p ${XUNFENG_DB}
nohup mongod --port 65521 --dbpath=${XUNFENG_DB} --auth > ${XUNFENG_LOG}/db.log &
nohup python ./Run.py > ${XUNFENG_LOG}/web.log &
nohup python ./aider/Aider.py > ${XUNFENG_LOG}/aider.log &
nohup python ./nascan/NAScan.py > ${XUNFENG_LOG}/scan.log &
nohup python ./vulscan/VulScan.py > ${XUNFENG_LOG}/vul.log &
可以看到主要起了如下四个服务
Run.py
from views.View import app
if __name__ == '__main__':
#app.debug = True
app.run(threaded=True, port=80,host='0.0.0.0')
webserver可以看出这个是flask起的web端,里面主要是做一些数据的展示和修改的。由于不是扫描器的重点,这里就不具体分析了,可以自己看下代码。
Aider.py
辅助验证脚本,一个50行左右的单文件,使用socket完成了一个简单的DNS log平台。
NAScan.py
网络资产信息抓取引擎 主要是调用nascan这个模块来进行网络资产(存活主机、开发端口、服务)的扫描。
VulScan.py
漏洞检测引擎 主要是调用vulscan/vuldb中的poc进行漏洞检测。
nascan
模块结构
─nascan
│ NAScan.py # 网络资产信息抓取引擎
│
├─lib
│ common.py 其他方法
│ icmp.py # ICMP发送类
│ log.py # 日志输出
│ mongo.py # 数据库连接
│ scan.py # 扫描与识别
│ start.py # 线程控制
└─plugin
masscan.py # 调用Masscan脚本从NAScan.py文件入口
# coding:utf-8
# author:wolf@YSRC
import thread
from lib.common import *
from lib.start import *
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
CONFIG_INI = get_config() # 读取配置
log.write('info', None, 0, u'获取配置成功') # 日志记录
STATISTICS = get_statistics() # 读取统计信息
MASSCAN_AC = [0] # 标识符 masscan是否在使用
NACHANGE = [0] # 标识符 扫描列表是否被改变
thread.start_new_thread(monitor, (CONFIG_INI,STATISTICS,NACHANGE)) # 心跳线程
thread.start_new_thread(cruise, (STATISTICS,MASSCAN_AC)) # 失效记录删除线程
socket.setdefaulttimeout(int(CONFIG_INI['Timeout']) / 2) # 设置连接超时
ac_data = []
while True:
now_time = time.localtime()
now_hour = now_time.tm_hour
now_day = now_time.tm_mday
now_date = str(now_time.tm_year) + str(now_time.tm_mon) + str(now_day)
cy_day, ac_hour = CONFIG_INI['Cycle'].split('|')
log.write('info', None, 0, u'扫描规则: ' + str(CONFIG_INI['Cycle']))
if (now_hour == int(ac_hour) and now_day % int(cy_day) == 0 and now_date not in ac_data) or NACHANGE[0]: # 判断是否进入扫描时段
ac_data.append(now_date)
NACHANGE[0] = 0
log.write('info', None, 0, u'开始扫描')
s = start(CONFIG_INI)
s.masscan_ac = MASSCAN_AC
s.statistics = STATISTICS
s.run() # 开始扫描
time.sleep(60)
except Exception, e:
print e
准备工作
一开始是获取配置信息
def get_config():
config = {}
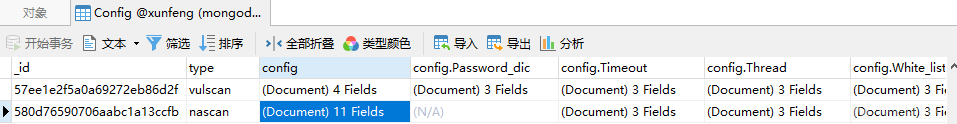
# 从mongodb中读取`nascan`的配置,可以从navicat中看到Config集合中有`vulscan`和`nascan`的扫描配置
config_info = mongo.na_db.Config.find_one({"type": "nascan"})
for name in config_info['config']:
# 对于cms识别、组件容器、动态语言、服务 的配置存储是使用`|`进行分割存储的
# 所以在取出之前要进行简单的格式化然后放到配置中
if name in ['Discern_cms', 'Discern_con', 'Discern_lang', 'Discern_server']:
config[name] = format_config(name, config_info['config'][name]['value'])
else:
config[name] = config_info['config'][name]['value']
return config
然后是进行日志记录
# coding:utf-8
import threading
import time
import sys
reload(sys)
sys.setdefaultencoding('utf8')
mutex = threading.Lock() # 线程互斥锁
def write(scan_type, host, port, info):
mutex.acquire() # 上锁,避免多个进程输出,导致格式混乱
port = int(port)
try: # 由于Run.sh中使用了nohup,所以`print`的输出会被输出到log文件中
time_str = time.strftime('%X', time.localtime(time.time()))
if scan_type == 'portscan':
print "[%s] %s:%d open" % (time_str, host, port)
elif scan_type == 'server':
print "[%s] %s:%d is %s" % (time_str, host, port, str(info))
elif scan_type == 'web':
print "[%s] %s:%d is web" % (time_str, host, port)
print "[%s] %s:%d web info %s" % (time_str, host, port, info)
elif scan_type == 'active':
print "[%s] %s active" % (time_str, host)
elif scan_type == 'info':
print "[%s] %s" % (time_str, info)
except Exception, e:
print 'logerror',e
pass
mutex.release()
之后进行读取统计信息
def get_statistics():
date_ = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
# 获取当日的统计信息
now_stati = mongo.na_db.Statistics.find_one({"date": date_})
if not now_stati:
# 没有当日的信息则返回一个初始统计信息
now_stati = {date_: {"add": 0, "update": 0, "delete": 0}}
return now_stati
else:
# 有则返回
return {date_: now_stati['info']}
两个监测线程
之后启动了两个现场,分别对应不同的功能
thread.start_new_thread(monitor, (CONFIG_INI,STATISTICS,NACHANGE)) # 心跳线程
thread.start_new_thread(cruise, (STATISTICS,MASSCAN_AC)) # 失效记录删除线程
monitor
monitor心跳线程,主要用于判断扫描配置是否发生了变化
def monitor(CONFIG_INI, STATISTICS, NACHANGE):
while True:
try:
time_ = datetime.datetime.now()
date_ = time_.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
# 记录心跳
mongo.na_db.Heartbeat.update({"name": "heartbeat"}, {"$set": {"up_time": time_}})
if date_ not in STATISTICS: STATISTICS[date_] = {"add": 0, "update": 0, "delete": 0}
# 更新统计信息
mongo.na_db.Statistics.update({"date": date_}, {"$set": {"info": STATISTICS[date_]}}, upsert=True)
new_config = get_config() # 获取最新配置
# 比较配置扫描列表的base64是否相同,不同则置NACHANGE[0]为1
if base64.b64encode(CONFIG_INI["Scan_list"]) != base64.b64encode(new_config["Scan_list"]):NACHANGE[0] = 1
CONFIG_INI.clear()
CONFIG_INI.update(new_config) # 更新新配置
except Exception, e:
print e
time.sleep(30) # 每30秒检测一次
回到NAScan.py中可以看到
# 判断是否达到了一个扫描的周期,或者心跳线程是否检测到扫描列表更新
# 因为上面可以看到base64不同时会将NACHANGE[0]置于1
# 至于为什么要传入NACHANGE[0]这样一个列表,而不是一个flag的int值(因为列表是引用啊!
if (now_hour == int(ac_hour) and now_day % int(cy_day) == 0 and now_date not in ac_data) or NACHANGE[0]:
cruise
然后是cruise 失效记录删除线程
def cruise(STATISTICS,MASSCAN_AC):
while True:
now_str = datetime.datetime.now()
week = int(now_str.weekday())
hour = int(now_str.hour)
if week >= 1 and week <= 5 and hour >= 9 and hour <= 18: # 非工作时间不删除
try:
# 获取扫描信息记录
data = mongo.NA_INFO.find().sort("time", 1)
for history_info in data:
while True:
# 如果masscan正在扫描即不进行清理
# 在后期可以看到在用masscan进行扫描的时候会置1
if MASSCAN_AC[0]:
time.sleep(10)
else:
break
ip = history_info['ip']
port = history_info['port']
try:
# 检测端口是否存活
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.connect((ip, int(port)))
sock.close()
except Exception, e:
time_ = datetime.datetime.now()
date_ = time_.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
# 不存活则删除改记录
mongo.NA_INFO.remove({"ip": ip, "port": port})
log.write('info', None, 0, '%s:%s delete' % (ip, port)) # 日志记录
STATISTICS[date_]['delete'] += 1
del history_info["_id"]
history_info['del_time'] = time_
history_info['type'] = 'delete'
# 添加一条操作历史
mongo.NA_HISTORY.insert(history_info)
except:
pass
time.sleep(3600) # 60分钟检测一次
start.py
回到NAScan.py, 前期的一些工作已经做完了,后面就可以进入while True的扫描循环了
now_time = time.localtime()
now_hour = now_time.tm_hour
now_day = now_time.tm_mday
now_date = str(now_time.tm_year) + str(now_time.tm_mon) + str(now_day)
# 获取资产探测周期
cy_day, ac_hour = CONFIG_INI['Cycle'].split('|')
log.write('info', None, 0, u'扫描规则: ' + str(CONFIG_INI['Cycle']))
if (now_hour == int(ac_hour) and now_day % int(cy_day) == 0 and now_date not in ac_data) or NACHANGE[0]: # 判断是否进入扫描时段
ac_data.append(now_date) # 判断是否扫描过的列表
NACHANGE[0] = 0 # 置0,
log.write('info', None, 0, u'开始扫描')
s = start(CONFIG_INI)
s.masscan_ac = MASSCAN_AC
s.statistics = STATISTICS
s.run() # 开始扫描
time.sleep(60)
s = start(CONFIG_INI)初始化了一个start类
class start:
def __init__(self, config):
# 传入CONFIG_INI 配置,然后设置类的属性
self.config_ini = config
self.queue = Queue.Queue()
self.thread = int(self.config_ini['Thread'])
self.scan_list = self.config_ini['Scan_list'].split('\n')
self.mode = int(self.config_ini['Masscan'].split('|')[0])
self.icmp = int(self.config_ini['Port_list'].split('|')[0])
self.white_list = self.config_ini.get('White_list', '').split('\n')
然后回来额外设置了masscan_ac和statistics两个引用标识符(因为要与其他线程共享对它的修改,相当于全局变量
然后启动s.run()开始扫描
def run(self):
# 在start.py中定义的全局变量,端口列表
global AC_PORT_LIST
all_ip_list = []
for ip in self.scan_list:
# 处理CIDR格式的ip, eg:192.168.0.1/24
# 就不具体跟进看了,大约40行左右,涉及一些位运算格式转换啥的
if "/" in ip: ip = cidr.CIDR(ip)
if not ip:continue
# 处理 192.168.0.1-192.168.0.255 这类范围ip
ip_list = self.get_ip_list(ip)
# 对于白名单ip进行移除
for white_ip in self.white_list:
if white_ip in ip_list:
ip_list.remove(white_ip)
# 是否开始了masscan扫描,开启了mode置为1,否则为0
if self.mode == 1: # 使用masscan扫描
# 获取文件路径
self.masscan_path = self.config_ini['Masscan'].split('|')[2]
# 获取扫描速率
self.masscan_rate = self.config_ini['Masscan'].split('|')[1]
# 获取存活的ip
ip_list = self.get_ac_ip(ip_list)
self.masscan_ac[0] = 1
AC_PORT_LIST = self.masscan(ip_list) # 如果安装了Masscan即使用Masscan进行全端口扫描
if not AC_PORT_LIST: continue
self.masscan_ac[0] = 0
for ip_str in AC_PORT_LIST.keys(): self.queue.put(ip_str) # 加入队列
self.scan_start() # 开始扫描
else:
all_ip_list.extend(ip_list)
if self.mode == 0: # 不使用masscan扫描
if self.icmp: all_ip_list = self.get_ac_ip(all_ip_list)
for ip_str in all_ip_list: self.queue.put(ip_str) # 加入队列
self.scan_start() # TCP探测模式开始扫描
探测存活ip
self.get_ac_ip()是通过ping请求来探测主机存活,后期只对存活主机进行扫描
def get_ac_ip(self, ip_list):
try:
s = icmp.Nscan()
ipPool = set(ip_list)
return s.mPing(ipPool)
except Exception, e:
print 'The current user permissions unable to send icmp packets'
return ip_list
跟到s.mPing()中
def mPing(self, ipPool):
# 获得icmp的socket
Sock = self.__icmpSocket
Sock.settimeout(self.timeout)
# 设置icmp数据报
packet = self.__icmpPacket
recvFroms = set()
# 初始化一个多线程的icmp请求类
sendThr = SendPingThr(ipPool, packet, Sock, self.timeout)
# 启动多线程icmp扫描
sendThr.start()
while True:
try:
# 获取返回的ip地址
ac_ip = Sock.recvfrom(1024)[1][0]
if ac_ip not in recvFroms:
log.write("active", ac_ip, 0, None)
# 添加存活ip到`recvForms`
recvFroms.add(ac_ip)
except Exception:
pass
finally:
if not sendThr.isAlive():
break
# 返回两个集合的交集
return recvFroms & ipPool
SendPingThr类
class SendPingThr(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, ipPool, icmpPacket, icmpSocket, timeout=3):
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.Sock = icmpSocket
self.ipPool = ipPool
self.packet = icmpPacket
self.timeout = timeout
self.Sock.settimeout(timeout + 1)
def run(self):
for ip in self.ipPool:
try:
self.Sock.sendto(self.packet, (ip, 0))
except socket.timeout:
break
except:
pass
time.sleep(self.timeout)
masscan扫描全端口
这样就依次将存活的ip返回到了start.py中的run()中
# 获取到返回的存活ip
ip_list = self.get_ac_ip(ip_list)
# 将masscan_ac[0]置1,表示masscan正在使用
self.masscan_ac[0] = 1
# 利用masscan进行全端口扫描
AC_PORT_LIST = self.masscan(ip_list)
if not AC_PORT_LIST: continue
# 将masscan_ac[0]置0
self.masscan_ac[0] = 0
for ip_str in AC_PORT_LIST.keys(): self.queue.put(ip_str) # 加入队列
self.scan_start() # 开始扫描
跟进self.masscan()函数
def masscan(self, ip):
try:
if len(ip) == 0: return
sys.path.append(sys.path[0] + "/plugin")
m_scan = __import__("masscan")
result = m_scan.run(ip, self.masscan_path, self.masscan_rate)
return result
except Exception, e:
print e
print 'No masscan plugin detected'
跟进m_scan.run()
import os
def run(ip_list,path,rate):
try:
ip_file = open('target.log','w')
# 将存活的ip列表写到target.log中
ip_file.write("\n".join(ip_list))
ip_file.close()
# 进行过滤一些危险字符
#(issue中也有提到,并不能完全保证后台的安全,主要还是保证对密钥的管理
path = str(path).translate(None, ';|&`\n')
rate = str(rate).translate(None, ';|&`\n')
if not os.path.exists(path):return
# 用系统命令进行masscan全端口扫描
os.system("%s -p1-65535 -iL target.log -oL tmp.log --randomize-hosts --rate=%s"%(path,rate))
# 读取扫描结果
result_file = open('tmp.log', 'r')
result_json = result_file.readlines()
result_file.close()
del result_json[0]
del result_json[-1]
open_list = {}
# 对扫描结果进行格式化处理
for res in result_json:
try:
ip = res.split()[3]
port = res.split()[2]
if ip in open_list:
open_list[ip].append(port)
else:
open_list[ip] = [port]
except:pass
os.remove('target.log')
os.remove('tmp.log')
# 返回扫描结果
return open_list
except:
pass
这样,再次回到start.py的run()中
# 用masscan进行全端口扫描
AC_PORT_LIST = self.masscan(ip_list)
if not AC_PORT_LIST: continue
# 将self.masscan_ac[0]置0,表示结束使用
self.masscan_ac[0] = 0
# 将扫描结果存入队列中
for ip_str in AC_PORT_LIST.keys(): self.queue.put(ip_str)
# 开始扫描
self.scan_start()
scan.py
前期准备
self.scan_start()
def scan_start(self):
for i in range(self.thread): # 开始扫描
t = ThreadNum(self.queue)
t.setDaemon(True)
t.mode = self.mode
t.config_ini = self.config_ini
t.statistics = self.statistics
t.start()
self.queue.join()
跟进ThreadNum类
class ThreadNum(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self, queue):
# 赋值扫描队列
threading.Thread.__init__(self)
self.queue = queue
def run(self):
while True:
try:
# 非阻塞模式
task_host = self.queue.get(block=False)
except:
break
try:
if self.mode:
# 开启masscan扫描则使用扫描出的存活端口
port_list = AC_PORT_LIST[task_host]
else:
# 否则扫描特定的端口
port_list = self.config_ini['Port_list'].split('|')[1].split('\n')
_s = scan.scan(task_host, port_list) # 初始化scan
_s.config_ini = self.config_ini # 提供配置信息
_s.statistics = self.statistics # 提供统计信息
_s.run() # 启动
except Exception, e:
print e
finally:
self.queue.task_done()
跟到scan类的run()方法中
def run(self):
self.timeout = int(self.config_ini['Timeout']) # 获取timeout
for _port in self.port_list:
self.server = ''
self.banner = ''
self.port = int(_port)
self.scan_port() # 端口扫描
if not self.banner:continue #无banner则跳过(`NULL`表示暂未检测出,不会continue
self.server_discern() # 服务识别
if self.server == '':
web_info = self.try_web() # 尝试web访问
if web_info:
# log记录
log.write('web', self.ip, self.port, web_info)
time_ = datetime.datetime.now()
# 将扫描结果存入mongodb
mongo.NA_INFO.update({'ip': self.ip, 'port': self.port},
{"$set": {'banner': self.banner, 'server': 'web', 'webinfo': web_info,
'time': time_}})
端口扫描
先是进行了self.scan_port()端口扫描
def scan_port(self):
try:
# 进行socket连接
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
sock.connect((self.ip, self.port))
time.sleep(0.2)
except Exception, e:
return
try:
# 获取banner信息
self.banner = sock.recv(1024)
sock.close()
# 小于等于2则置为'NULL'
if len(self.banner) <= 2:
self.banner = 'NULL'
except Exception, e:
# 异常情况也置为'NULL'
self.banner = 'NULL'
# 日志记录
log.write('portscan', self.ip, self.port, None)
banner = ''
hostname = self.ip2hostname(self.ip)
time_ = datetime.datetime.now()
date_ = time_.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
try:
# 进行unicode转换
banner = unicode(self.banner, errors='replace')
if self.banner == 'NULL': banner = ''
# 添加一条info信息
mongo.NA_INFO.insert({"ip": self.ip, "port": self.port, "hostname": hostname, "banner": banner, "time": time_})
# 统计信息+1
self.statistics[date_]['add'] += 1
except:
if banner:
# 原子操作,删除已存在的记录
history_info = mongo.NA_INFO.find_and_modify(
query={"ip": self.ip, "port": self.port, "banner": {"$ne": banner}}, remove=True)
if history_info:
# 新增info记录
mongo.NA_INFO.insert(
{"ip": self.ip, "port": self.port, "hostname": hostname, "banner": banner, "time": time_})
# 统计信息+1
self.statistics[date_]['update'] += 1
# 删除原先的_id
del history_info["_id"]
history_info['del_time'] = time_
history_info['type'] = 'update'
# 更新type和del_time之后插入一条新历史记录
mongo.NA_HISTORY.insert(history_info)
进行socket连接的时候,例如一些ssh之类的服务,会返回一些banner信息
服务识别
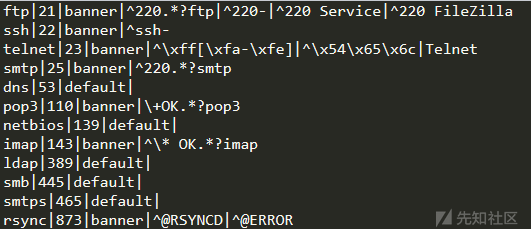
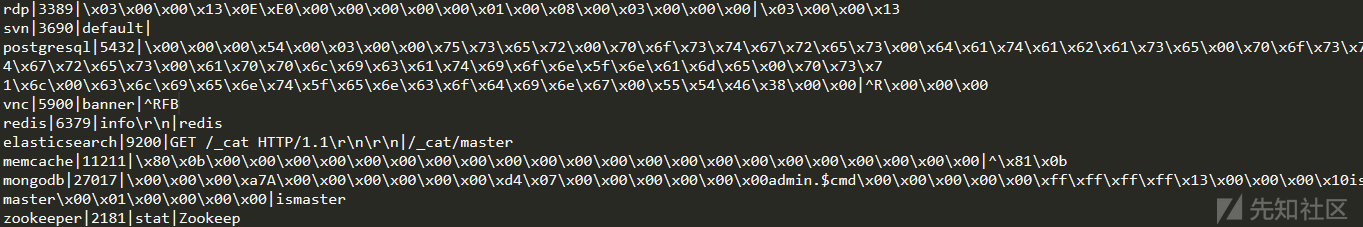
def server_discern(self):
# 先尝试进行利用配置中的`Discern_server`进行快速匹配识别
for mark_info in self.config_ini['Discern_server']:
try:
name, default_port, mode, reg = mark_info
if mode == 'default':
# default表示用特定端口,匹配特定服务
if int(default_port) == self.port:
self.server = name
elif mode == 'banner':
# 利用banner信息进行正则匹配检测
matchObj = re.search(reg, self.banner, re.I | re.M)
if matchObj:
self.server = name
if self.server:break
except:
continue
# 对于未检测出服务并且端口不为80、443、8080的端口进行检测
if not self.server and self.port not in [80,443,8080]:
for mark_info in self.config_ini['Discern_server']: # 发包识别
try:
name, default_port, mode, reg = mark_info
if mode not in ['default','banner']:
# 进行发送特定的socket包获取banner信息,进行再次匹配
dis_sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
dis_sock.connect((self.ip, self.port))
mode = mode.decode('string_escape')
reg = reg.decode('string_escape')
dis_sock.send(mode)
time.sleep(0.3)
dis_recv = dis_sock.recv(1024)
dis_sock.close()
matchObj = re.search(reg, dis_recv, re.I | re.M)
if matchObj:
self.server = name
break
except:
pass
if self.server:
# 对于检测到的服务,进行log和info的记录
log.write("server", self.ip, self.port, self.server)
mongo.NA_INFO.update({"ip": self.ip, "port": self.port}, {"$set": {"server": self.server}})
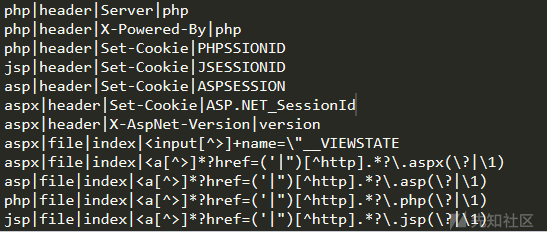
config_ini['Discern_server']中的值
config_ini['Discern_server']中的特定socket数据包
web访问
def try_web(self):
title_str, html = '', ''
try:# 进行http/https请求,获取响应报文
if self.port == 443:
# 对于443端口的使用https协议
info = urllib2.urlopen("https://%s:%s" % (self.ip, self.port), timeout=self.timeout)
else:
info = urllib2.urlopen("http://%s:%s" % (self.ip, self.port), timeout=self.timeout)
html = info.read()
header = info.headers
except urllib2.HTTPError, e:
html = e.read()
header = e.headers
except:
return
if not header: return
# 对于gzip格式的响应,进行解压gzip
if 'Content-Encoding' in header and 'gzip' in header['Content-Encoding']:
html_data = StringIO.StringIO(html)
gz = gzip.GzipFile(fileobj=html_data)
html = gz.read()
try:
# 格式转码
html_code = self.get_code(header, html).strip()
if html_code and len(html_code) < 12:
html = html.decode(html_code).encode('utf-8')
except: pass
try:
# 获取titile信息
title = re.search(r'<title>(.*?)</title>', html, flags=re.I | re.M)
if title: title_str = title.group(1)
except: pass
try:
# 将响应的http报文设置成banner信息
web_banner = str(header) + "\r\n\r\n" + html
self.banner = web_banner
# 添加记录
history_info = mongo.NA_INFO.find_one({"ip": self.ip, "port": self.port})
if 'server' not in history_info:
tag = self.get_tag()
web_info = {'title': title_str, 'tag': tag}
return web_info
else:
if abs(len(history_info['banner'].encode('utf-8')) - len(web_banner)) > len(web_banner) / 60:
del history_info['_id']
history_info['del_time'] = datetime.datetime.now()
mongo.NA_HISTORY.insert(history_info)
tag = self.get_tag()
web_info = {'title': title_str, 'tag': tag}
date_ = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
self.statistics[date_]['update'] += 1
log.write('info', None, 0, '%s:%s update web info'%(self.ip, self.port))
return web_info
except:
return
get_tag()
def get_tag(self):
try:
url = self.ip + ':' + str(self.port)
# 对web服务进行cms、组件容器、动态语言的识别
tag = map(self.discern, ['Discern_cms', 'Discern_con', 'Discern_lang'], [url, url, url])
# 过滤掉未识别出的服务
return filter(None, tag)
except Exception, e:
return
discern()
def discern(self, dis_type, domain):
file_tmp = {}
if int(domain.split(":")[1]) == 443: # http/https处理
protocol = "https://"
else:
protocol = "http://"
try:
# http请求
req = urllib2.urlopen(protocol + domain, timeout=self.timeout)
header = req.headers
html = req.read()
except urllib2.HTTPError, e:
html = e.read()
header = e.headers
except Exception, e:
return
# 对于'Discern_cms', 'Discern_con', 'Discern_lang'在数据库中都有自己的识别判断方式
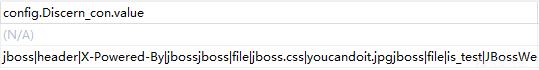
for mark_info in self.config_ini[dis_type]:
if mark_info[1] == 'header':
try:
if not header: return
# 通过header方式则对对应的http头中的值进行匹配
# 如存在PHPSSIONID之类的值判定为php
if re.search(mark_info[3], header[mark_info[2]], re.I):
return mark_info[0]
except Exception, e:
continue
elif mark_info[1] == 'file':
if mark_info[2] == 'index':
try:
if not html: return
# 对于file index方式利用文件后缀,如1.php这样判断为php语言
if re.search(mark_info[3], html, re.I):
return mark_info[0]
except Exception, e:
continue
else:
# 防止重复检测
if mark_info[2] in file_tmp:
re_html = file_tmp[mark_info[2]]
else:
# 访问指定的robots.txt之类的文件
try:
re_html = urllib2.urlopen(protocol + domain + "/" + mark_info[2],
timeout=self.timeout).read()
except urllib2.HTTPError, e:
re_html = e.read()
except Exception, e:
return
file_tmp[mark_info[2]] = re_html
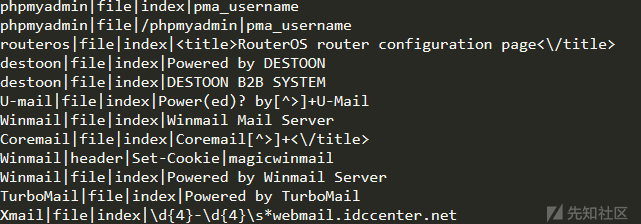
try:
# 检测指定文件中是否存在特定关键字
# 如robots.txt中存在'php168'则为php168cms
if re.search(mark_info[3], re_html, re.I):
return mark_info[0]
except Exception, e:
print mark_info[3]
config_ini[Discern_lang]中的值
config_ini[Discern_cms]中的值
最后回到run()中
web_info = self.try_web() # 尝试web访问
if web_info:
# 检测完web特征之后,就是进行简单的log记录,和更新数据库中info的值
log.write('web', self.ip, self.port, web_info)
time_ = datetime.datetime.now()
mongo.NA_INFO.update({'ip': self.ip, 'port': self.port},
{"$set": {'banner': self.banner, 'server': 'web', 'webinfo': web_info,
'time': time_}})
到这里,scan的扫描也就结束了,回到start类的run()中,剩下的就是不使用masscan的扫描
if self.mode == 0: # 不使用masscan扫描
# 如果设置了icmp检测,会对ip列表进行存活检测,只扫描存活ip
if self.icmp: all_ip_list = self.get_ac_ip(all_ip_list)
for ip_str in all_ip_list: self.queue.put(ip_str) # 加入队列
self.scan_start() # TCP探测模式开始扫描
这里的扫描过程中将ip列表改成了all_ip_list,其余的扫描过程也是通过scan_start()来调用scan类进行扫描。
到这里,整个NAScan资产扫描过程也就完成了,每次扫描完会sleep60秒,然后再次循环这个过程。
vulscan
用于对扫出的资产进行漏洞扫描,具体的扫描过程依赖于vuldb中的插件形式进行扫描,做到可插拔的模式
json格式的插件
转换成json形式后就是
{
"name" : "Axis2信息泄露",
"info" : "HappyAxis.jsp 页面存在系统敏感信息。",
"level" : "低危",
"type" : "信息泄露",
"author" : "wolf@YSRC",
"url": "",
"keyword" : "tag:axis2",
"source" : 1,
"plugin" : {
"url" : "/axis2/axis2-web/HappyAxis.jsp",
"tag" : "敏感信息泄露",
"analyzing" : "keyword",
"analyzingdata" : "Axis2 Happiness Page",
"data" : "",
"method" : "GET"
}
}
python脚本格式的插件
# coding:utf-8
import ftplib
def get_plugin_info(): # 插件描述信息
plugin_info = {
"name": "FTP弱口令",
"info": "导致敏感信息泄露,严重情况可导致服务器被入侵控制。",
"level": "高危",
"type": "弱口令",
"author": "wolf@YSRC",
"url": "",
"keyword": "server:ftp", # 推荐搜索关键字
}
return plugin_info
def check(ip, port, timeout): # 漏洞检测代码
user_list = ['ftp', 'www', 'admin', 'root', 'db', 'wwwroot', 'data', 'web']
for user in user_list:
for pass_ in PASSWORD_DIC: # 密码字典无需定义,程序会自动为其赋值。
pass_ = str(pass_.replace('{user}', user))
try:
ftp = ftplib.FTP()
ftp.timeout = timeout
ftp.connect(ip, port)
ftp.login(user, pass_)
if pass_ == '': pass_ = 'null'
if user == 'ftp' and pass_ == 'ftp': return u"可匿名登录"
return u"存在弱口令,账号:%s,密码:%s" % (user, pass_) # 成功返回结果,内容显示在扫描结果页面。
except:
pass
扫描过程较资产扫描偏简单些,一个280行左右的单文件
一开始定义了一些全局变量
# 添加系统路径
sys.path.append(sys.path[0] + '/vuldb')
sys.path.append(sys.path[0] + "/../")
# 获取mongodb账号配置
from Config import ProductionConfig
# 进行mongodb认证连接
db_conn = pymongo.MongoClient(ProductionConfig.DB, ProductionConfig.PORT)
na_db = getattr(db_conn, ProductionConfig.DBNAME)
na_db.authenticate(ProductionConfig.DBUSERNAME, ProductionConfig.DBPASSWORD)
# 做了几个集合的简化操作
na_task = na_db.Task
na_result = na_db.Result
na_plugin = na_db.Plugin
na_config = na_db.Config
na_heart = na_db.Heartbeat
# 线程锁
lock = thread.allocate()
# 一些全局变量
PASSWORD_DIC = []
THREAD_COUNT = 50
TIMEOUT = 10
PLUGIN_DB = {}
TASK_DATE_DIC = {}
WHITE_LIST = []
然后开始运行流程
if __name__ == '__main__':
init() # 进行init初始化操作
PASSWORD_DIC, THREAD_COUNT, TIMEOUT, WHITE_LIST = get_config() # 获取配置
thread.start_new_thread(monitor, ()) # 启动监控线程
while True:
task_id, task_plan, task_target, task_plugin = queue_get() # 任务信息获取
if task_id == '':
time.sleep(10)
continue
if PLUGIN_DB:
del sys.modules[PLUGIN_DB.keys()[0]] # 清理插件缓存
PLUGIN_DB.clear()
for task_netloc in task_target:
while True:
if int(thread._count()) < THREAD_COUNT:
if task_netloc[0] in WHITE_LIST: break
thread.start_new_thread(vulscan, (task_id, task_netloc, task_plugin))
break
else:
time.sleep(2)
if task_plan == 0: na_task.update({"_id": task_id}, {"$set": {"status": 2}})
准备工作
init
用于获取插件的信息
def init():
# 若数据库中存在插件信息,则直接返回,否则重新获取
if na_plugin.find().count() >= 1: return
script_plugin = []
json_plugin = []
# 获取vuldb中的插件
file_list = os.listdir(sys.path[0] + '/vuldb')
time_ = datetime.datetime.now()
for filename in file_list:
try:
# 插件分为json和py两种格式
if filename.split('.')[1] == 'py':
script_plugin.append(filename.split('.')[0])
if filename.split('.')[1] == 'json':
json_plugin.append(filename)
except:
pass
for plugin_name in script_plugin:
try:
# py格式的插件直接导入,然后读取对于变量,插入到mongodb中
res_tmp = __import__(plugin_name)
plugin_info = res_tmp.get_plugin_info()
plugin_info['add_time'] = time_
plugin_info['filename'] = plugin_name
plugin_info['count'] = 0
na_plugin.insert(plugin_info)
except:
pass
for plugin_name in json_plugin:
try:
# json格式的插件,用json解析后读取对应变量,插入到mongodb中
json_text = open(sys.path[0] + '/vuldb/' + plugin_name, 'r').read()
plugin_info = json.loads(json_text)
plugin_info['add_time'] = time_
plugin_info['filename'] = plugin_name
plugin_info['count'] = 0
del plugin_info['plugin']
na_plugin.insert(plugin_info)
except:
pass
get_config
def get_config():
try:
config_info = na_config.find_one({"type": "vulscan"})
pass_row = config_info['config']['Password_dic']
thread_row = config_info['config']['Thread']
timeout_row = config_info['config']['Timeout']
white_row = config_info['config']['White_list']
password_dic = pass_row['value'].split('\n')
thread_count = int(thread_row['value'])
timeout = int(timeout_row['value'])
white_list = white_row['value'].split('\n')
return password_dic, thread_count, timeout, white_list
except Exception, e:
print e
和之前nascan中的读取配置类似,只是这回读的是type为vulscan的配置
读取弱口令、线程数、timeout、白名单之类的配置参数,然后返回
monitor
新起了个monitor监测线程,监测插件的使用情况
def monitor():
# 引入全局变量
global PASSWORD_DIC, THREAD_COUNT, TIMEOUT, WHITE_LIST
while True:
# 获取正在执行的任务
queue_count = na_task.find({"status": 0, "plan": 0}).count()
if queue_count:
# 如果有正在执行的任务,则置为1
load = 1
else:
# 否则根据当前线程数,来判断插件是否在被使用
ac_count = thread._count()
load = float(ac_count - 4) / THREAD_COUNT
if load > 1: load = 1
if load < 0: load = 0
# 更新mongodb中的heatbeat集合,有插件正在扫描
na_heart.update({"name": "load"}, {"$set": {"value": load, "up_time": datetime.datetime.now()}})
PASSWORD_DIC, THREAD_COUNT, TIMEOUT, WHITE_LIST = get_config()
# 然后根据load值进行不同时间的休眠
if load > 0:
time.sleep(8)
else:
time.sleep(60)
然后进入到while True的循环
通过queue_get()进行任务参数的获取
def queue_get():
global TASK_DATE_DIC
# 获取未加载的task,更新为启动状态
task_req = na_task.find_and_modify(query={"status": 0, "plan": 0}, update={"$set": {"status": 1}}, sort={'time': 1})
if task_req:
# 如果存在,在TASK_DATE_DIC记录task,然后返回任务信息
TASK_DATE_DIC[str(task_req['_id'])] = datetime.datetime.now()
return task_req['_id'], task_req['plan'], task_req['target'], task_req['plugin']
else:
# 获取 plan != 0 的task列表
task_req_row = na_task.find({"plan": {"$ne": 0}})
if task_req_row:
for task_req in task_req_row:
# 判断是否需要再次启动任务
if (datetime.datetime.now() - task_req['time']).days / int(task_req['plan']) >= int(task_req['status']):
if task_req['isupdate'] == 1:
# 任务更新后,需要重新从info集合中获取ip和port
# 更新task集合的target
task_req['target'] = update_target(json.loads(task_req['query']))
na_task.update({"_id": task_req['_id']}, {"$set": {"target": task_req['target']}})
# 更新task集合中的status自增1
na_task.update({"_id": task_req['_id']}, {"$inc": {"status": 1}})
# 在TASK_DATE_DIC记录task
TASK_DATE_DIC[str(task_req['_id'])] = datetime.datetime.now()
# 返回task信息
return task_req['_id'], task_req['plan'], task_req['target'], task_req['plugin']
return '', '', '', ''
回到__main__中
# 获取任务信息
task_id, task_plan, task_target, task_plugin = queue_get()
if task_id == '':
# 没有获取到task配置则sleep10秒后继续获取
time.sleep(10)
continue
if PLUGIN_DB:
# 当有插件缓存时清理插件缓存
# 后面扫描时会导入插件模块,删除之前导入的模块
del sys.modules[PLUGIN_DB.keys()[0]]
PLUGIN_DB.clear()
for task_netloc in task_target:
while True:
# 控制线程数
if int(thread._count()) < THREAD_COUNT:
# 剔除白名单ip
if task_netloc[0] in WHITE_LIST: break
# 启动vulscan扫描线程
thread.start_new_thread(vulscan, (task_id, task_netloc, task_plugin))
break
else:
time.sleep(2)
# task_plan == 0 为一次性任务
# 更新 status = 2
if task_plan == 0: na_task.update({"_id": task_id}, {"$set": {"status": 2}})
vulscan
__init__
def __init__(self, task_id, task_netloc, task_plugin):
self.task_id = task_id
self.task_netloc = task_netloc
self.task_plugin = task_plugin
self.result_info = ''
self.start()
设置好类变量,然后进入start()
def start(self):
self.get_plugin_info()
if '.json' in self.plugin_info['filename']: # json检测模式
try:
self.load_json_plugin() # 读取漏洞标示
self.set_request() # 标示符转换为请求
self.poc_check() # 检测
except Exception, e:
return
else: # py脚本检测模式
plugin_filename = self.plugin_info['filename']
self.log(str(self.task_netloc) + "call " + self.task_plugin)
if task_plugin not in PLUGIN_DB:
plugin_res = __import__(plugin_filename)
setattr(plugin_res, "PASSWORD_DIC", PASSWORD_DIC) # 给插件声明密码字典
PLUGIN_DB[plugin_filename] = plugin_res
try:
self.result_info = PLUGIN_DB[plugin_filename].check(str(self.task_netloc[0]), int(self.task_netloc[1]),TIMEOUT)
except:
return
self.save_request() # 保存结果
json格式检测
先load_json_plugin()加载配置脚本
def get_plugin_info(self):
info = na_plugin.find_one({"name": self.task_plugin})
self.plugin_info = info
然后转换为http请求,返回请求句柄
def set_request(self):
# 构建url
url = 'http://' + self.task_netloc[0] + ":" + str(self.task_netloc[1]) + self.plugin_info['plugin']['url']
if self.plugin_info['plugin']['method'] == 'GET':
# 进行GET请求
request = urllib2.Request(url)
else:
# 否则进行post请求
request = urllib2.Request(url, self.plugin_info['plugin']['data'])
self.poc_request = request
然后验证poc是否有效
def poc_check(self):
try:
# 进行http请求,获取header和body信息
res = urllib2.urlopen(self.poc_request, timeout=30)
res_html = res.read(204800)
header = res.headers
# res_code = res.code
except urllib2.HTTPError, e:
# res_code = e.code
header = e.headers
res_html = e.read(204800)
except Exception, e:
return
try:
# 获取编码,然后转码
html_code = self.get_code(header, res_html).strip()
if html_code and len(html_code) < 12:
res_html = res_html.decode(html_code).encode('utf-8')
except:
pass
an_type = self.plugin_info['plugin']['analyzing']
vul_tag = self.plugin_info['plugin']['tag']
analyzingdata = self.plugin_info['plugin']['analyzingdata']
if an_type == 'keyword':
# 如果是关键词检测,判断是正则还是MD5的检测,然后进行比对
if analyzingdata.encode("utf-8") in res_html: self.result_info = vul_tag
elif an_type == 'regex':
if re.search(analyzingdata, res_html, re.I): self.result_info = vul_tag
elif an_type == 'md5':
md5 = hashlib.md5()
md5.update(res_html)
# 比对成功,则返回插件tag
if md5.hexdigest() == analyzingdata: self.result_info = vul_tag
py脚本检测
# 获取插件文件名
plugin_filename = self.plugin_info['filename']
self.log(str(self.task_netloc) + "call " + self.task_plugin)
if task_plugin not in PLUGIN_DB:
# 不在PLUGIN_DB中则导入
plugin_res = __import__(plugin_filename)
setattr(plugin_res, "PASSWORD_DIC", PASSWORD_DIC) # 给插件声明密码字典
PLUGIN_DB[plugin_filename] = plugin_res # 添加到PLUGIN_DB中
try:
# 启用py脚本的check方法,并设置timeout
self.result_info = PLUGIN_DB[plugin_filename].check(str(self.task_netloc[0]), int(self.task_netloc[1]),TIMEOUT)
except:
return
保存请求结果
def save_request(self):
# 判断是否扫描出结果了
if self.result_info:
try:
time_ = datetime.datetime.now()
self.log(str(self.task_netloc) + " " + self.result_info)
# 没有这条扫描记录则插件扫出的记录+1
v_count = na_result.find(
{"ip": self.task_netloc[0], "port": self.task_netloc[1], "info": self.result_info}).count()
if not v_count: na_plugin.update({"name": self.task_plugin}, {"$inc": {'count': 1}})
vulinfo = {"vul_name": self.plugin_info['name'], "vul_level": self.plugin_info['level'],
"vul_type": self.plugin_info['type']}
w_vul = {"task_id": self.task_id, "ip": self.task_netloc[0], "port": self.task_netloc[1],
"vul_info": vulinfo, "info": self.result_info, "time": time_,
"task_date": TASK_DATE_DIC[str(self.task_id)]}
# 添加扫描结果记录
na_result.insert(w_vul)
except Exception, e:
pass
到此也就完成了vulscan的扫描过程。
最后
巡风中对于扫描的分工,多线程的处理都有很多值得学习和借鉴的地方。而且几乎都有增加一些心跳线程,用于监测。
分析中难免有些不足或者错误,欢迎大佬们指出!
Reference
https://landgrey.me/xunfeng-nascan-analysis/
原文链接:https://xz.aliyun.com/t/4104